Highly flexible and hugely scalable, NoSQL databases offer a range of data models and consistency options to suit your application
The modern sense of NoSQL, which dates from 2009, refers to databases that are not built on relational tables, unlike SQL databases. Often, NoSQL databases boast better design flexibility, horizontal scalability, and higher availability than traditional SQL databases, sometimes at the cost of weaker consistency.
NoSQL databases can take a number of forms. They can be cloud services or install on-premises. They can support one or more data models: key-value, document, column, graph, and sometimes even relational—which is one reason that NoSQL is sometimes parsed as “Not Only SQL.”
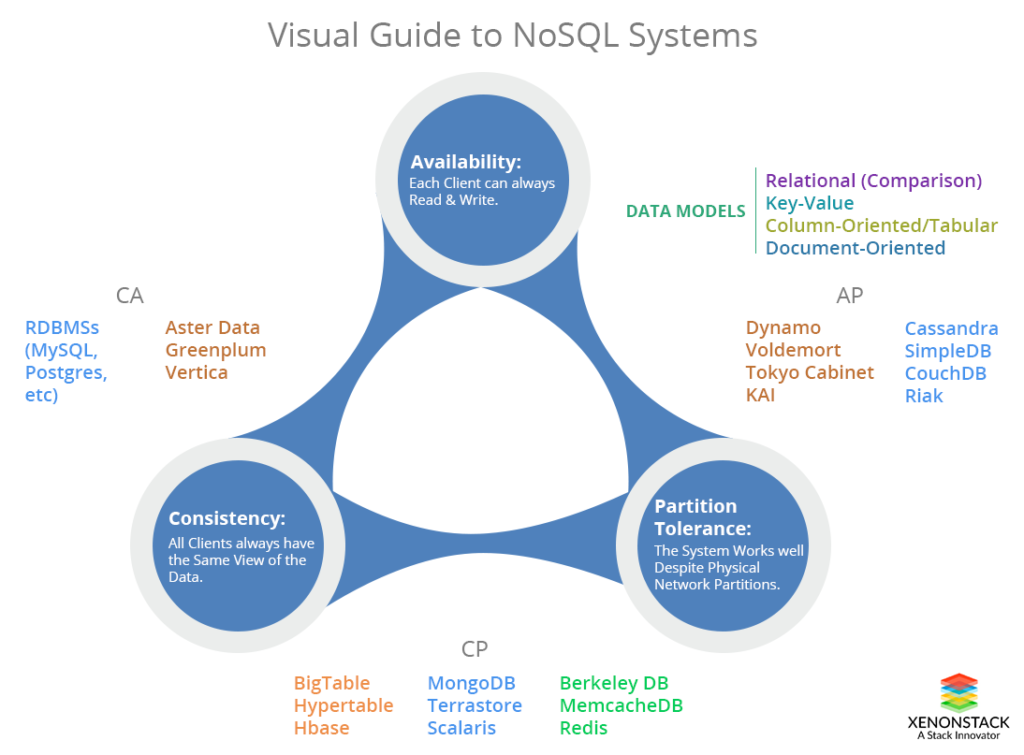
They can also support a range of consistency models, from strong consistency to eventual consistency.[ SQL databases are gaining NoSQL features. Discover 10 new tricks your old database can do. | Don’t miss these 7 powerful features in MySQL and MariaDB. | Keep up with hot topics in programming with InfoWorld’s App Dev Report newsletter. ]
Key-value is the most basic of the four non-relational data models. Sometimes other database models are implemented on top of a key-value foundation layer.
Column databases have keys, values, and timestamps; the timestamp is used for determining the valid content. Cassandra is a prominent example of a column database.



